The UX engineer role is becoming increasingly popular among many organizations. Companies are looking for a professional knowledgeable in UX design and development. In this article, we will learn what a UX engineer is and what skills are required to become one.
What is a UX engineer?
Before we jump into the role of UX engineer, it's essential to clarify what user experience really is. User experience encompasses all aspects of the user's interaction with a company and its product(s). When a user has pleasurable experience interacting with a product, they are more willing to use this product again and recommend it to others. A UX engineer plays an integral part in creating pleasurable user interaction with a digital product.
A UX engineer (user experience engineer) is a professional who focuses on technical elements of the user's experience. It's a hybrid of UX designers and software developers; in most organizations, UX engineering becomes a bridge between design and development. UX engineers aim to simplify human-computer interactions by applying the principles of good design when implementing a design.
The responsibilities of a UX engineer differ from one organization to another. Here is a general list of activities that UX engineers can be responsible for:
Creating wireframes or mockups of pages/screens
UX engineers design wireframes & low-/high-fidelity mockups of user interfaces using UX design tools. UX engineers typically do it with other teammates, such as UX or UI designers.
Creating coded prototypes of a design
UX engineers are often responsible for converting design assets they receive from UI designers into code. UX engineers can create interactive prototypes of a future product (such as a coded prototype of a website).
Evaluating the clarity of design
UX engineers make decisions about what to build and how to build it. For example, when a UX engineer evaluates a design of a button, they ask, "what label should we choose for this button so that the user can understand what it does?"
Evaluating the technical feasibility of the design
UX engineers are often invited to the conceptualization phase of the design process when designers discuss and evaluate different design solutions. Since UX engineers have development skills, they can help the design team evaluate a solution's feasibility and understand how hard it will be to implement it.
Creating and maintaining a design system
Design systems help product teams build consistent designs faster. UX engineers are typically responsible for creating and maintaining a design system because they know how to organize UI components and visual styles properly.
Advocate for design and development
UX engineers can advocate for good design both for designers and developers. The UX engineer's job is to reduce any potential friction during the design handoff, a procedure when designers share design assets with engineers.
Conducting usability testing
When UX engineers evaluate design, they know when they need more information about user behavior. UX engineers may conduct usability testing to understand better user needs or specifics of how they interact with a product.
The annual salary of a UX engineer can vary depending on the organization and projects. According to Glassdoor, the average annual salary of a UX engineer in the US in 2022 is $124k, ranging from 100k to 159k.
Is a UX engineer the same as a UX designer?
No, UX engineer and UX designer are two separate roles. UX designers are designers first—they design mockups/prototypes of a future product. UX designers rarely touch code when they create designs. UX engineers are engineers first—while they have a working knowledge of design, they typically work on the technical side of building interfaces. They have solid coding skills that allow them to build products with a good user experience.
Does a UX engineer require coding?
Yes, UX engineers should have solid coding skills. A UX engineer focus on the technical side of a user's experience. Most of the time, UX engineers are expected to have solid front-end development skills that allow them to build a product. The list of languages includes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Practical experience using the web or mobile frameworks can be a competitive advantage.
How to become a UX Engineer?
There are many skills that a person must master to become a UX engineer, and the exact skillset can vary depending on the company or a project that the UX engineer is working on. While reading this section, you might notice that some skills mentioned below are similar to those of a UX designer. However, the differences between UX design and UX engineering lie mainly in the technical skills required.
Here are the skills required to be successful as a UX engineer:
1. Front-end development skills
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are essential programming languages that any UX engineer should master to create effective solutions. UX engineers should also learn popular frameworks such as Bootstrap, Vue, and Angular to develop complex solutions faster. It's true that languages and frameworks evolve over time, but the foundational programming skills stay constant so that once the UX engineer learns how to code, they can easily use this knowledge when learning a new language/framework.
 Turning design into code. Image by Firos nv.
Turning design into code. Image by Firos nv.
2. Version control system
UX engineers use version control systems like Git or Bitbucket to store the codebase of their solutions. Version control can be applied to visual assets (i.e., the design of individual pages/screens of a product) and a design system. Version control makes it easier to introduce the changes in design and ensures that the product team has access to the latest version of the design.
3. Responsive design
Modern websites can be accessed on different types of devices—from a small screen of a mobile phone to the large screen of a TV. UX engineers should understand responsive design best practices to create a design that looks well on any screen size and resolution. Responsive design will require an in-depth understanding of CSS styles and CSS frameworks. Responsible design skills guarantee that UX engineers will create the proper web layout and use the right UI components to scale well.
4. UI design and prototyping
Depending on the stage of the product design process, UX engineers might need to create low or high-fidelity prototypes. It's helpful to have hands-on experience with prototyping tools, which allow UX engineers to turn low-fidelity prototypes into high-fidelity prototypes.
UX engineers should understand design systems well because the solutions UX engineers create should be both visually and functionally consistent. It means that UX engineers should clearly specify the visual and functional role of individual components and strive to reuse as many existing components/styles as possible.
5. Accessibility
When a product team designs a new product, they need to ensure that the product is accessible to all groups of users, including users with disabilities. UX engineers should be familiar with accessibility guidelines such as WCAG and have practical experience using accessibility tools such as WAVE. Accessibility knowledge will help UX engineers to ensure that they are creating an inclusive design, a design that works well for all groups of users.
6. Code debugging
Software testing is an essential part of the design process because it helps to identify and fix functional issues before the product ships. When it comes to UX engineering, testing means that a UX engineer should be able to debug coded prototypes to ensure that the solution functions technically well. UX engineers should be proficient with tools like Chrome DevTools to debug web pages.
Debugging using Chrome DevTools. Image by Google.
7. Empathy towards users and teammates
Empathy is the ability to understand and relate to other people's feelings. A UX engineer needs to empathize with end-users and the people they're working with. Empathy helps UX engineers put themselves in another team member's shoes. A strong sense of empathy will help create a product that will positively impact the users' lives and build trust in the design collective.
8. Communication and collaboration
As was mentioned above, a UX engineer is a bridge between design and development. UX engineer communicates and collaborates with design and development teams daily. Strong communication and collaboration skills will help UX engineers to present the design solution or share their professional opinion about something with others. When UX engineers present a solution, they use a language that both designers and developers understand.
9. Design thinking
UX engineers should be familiar with design thinking, a product design ideology that aims to create a user-centered design. Product creators who practice design thinking rely on a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem-solving and typically develop innovative solutions to existing problems. Design thinking helps product creators to combine what's desirable with what's technologically feasible. Design thinking motivates UX engineers to iterate and try various design decisions while implementing a design.
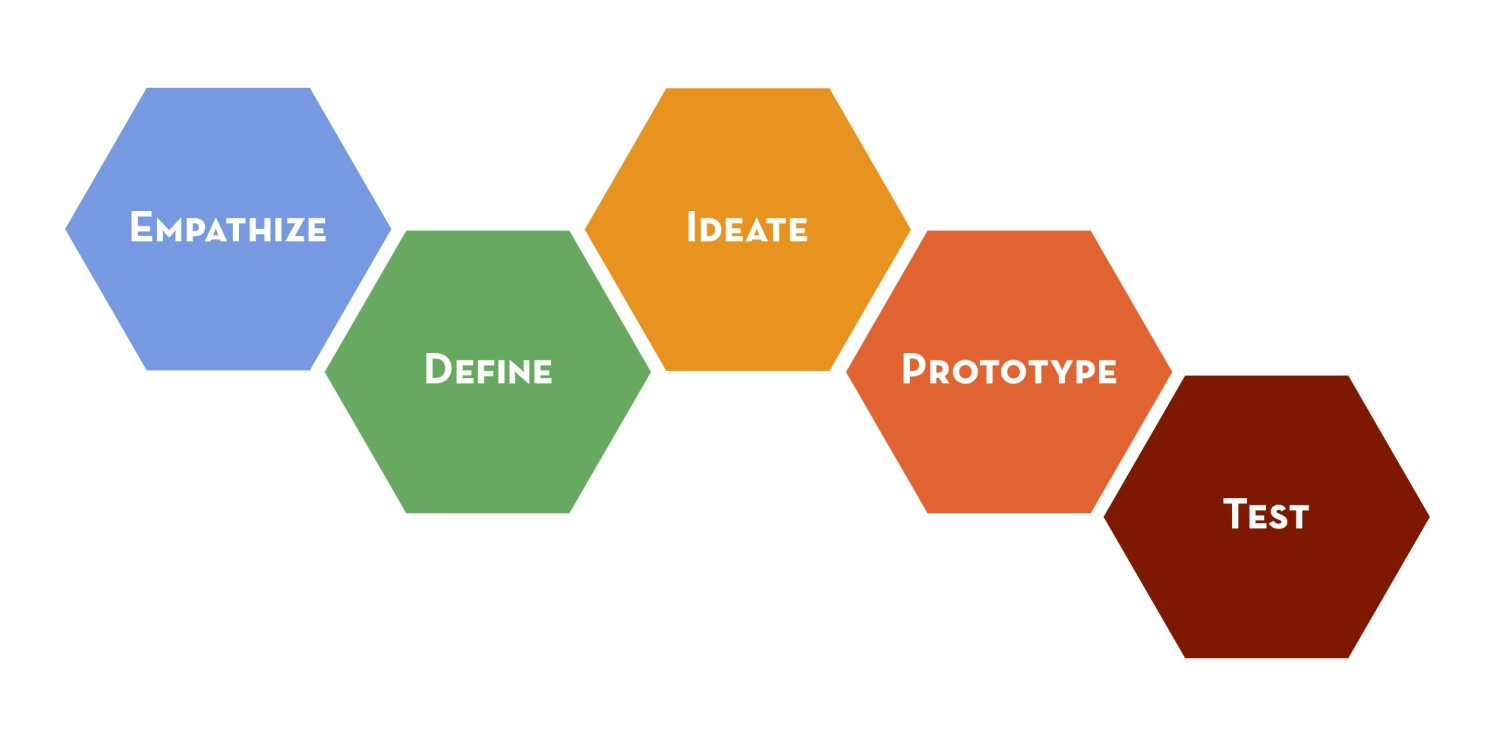
Design thinking: empathize, define, ideate, prototype and test. Image by Stanford d School.
10. User journey analysis
UX engineers should constantly evaluate design decisions in the context of the user journey, a path the user goes through when interacting with a product. This thinking helps create products with good navigation systems and incorporate the proper interaction patterns.

User journey map. Image by UX Indonesia.
11. Backlog prioritization
Backlog prioritization is a prerogative of project managers, but in many organizations, project managers discuss priorities with UX engineers. UX engineers know how much time it takes to implement something and what value it will bring to end users, and they can use this knowledge when prioritizing product design changes. UX engineers can help project managers balance priorities when it comes to turning design into code.
12. Foundational laws and principles of good product design
A good understanding of user interface design principles is highly valued in product design and development. Hick's and Fitts's laws, Peak-end-rule, and gestalt principles—are just a few laws and principles that UX engineers should be familiar with to design effective solutions. For example, when UX engineers code a button for a touch interface, they choose a size for a button to make it finger-friendly and place it in an area that will make it comfortable for users to interact with (by applying Fitts law and gestalt principles).
FAQ
Is a UX engineer the same as a front-end developer?
UX engineer and front-end developer roles have a lot in common, yet they are two different roles. A UX engineer's focus on technical elements of a user's experience separates this role from a front-end developer. Front-end developers can become UX engineers if they learn user experience principles and will use them when building a product.
What should I major in to become a UX engineer?
UX engineers should understand how products work inside and out. They should be proficient in both UX design and development. Many times, it's easier to move to UX engineering from web development because web developers have required coding skills and need to gain UX skills. So a UX engineer is expected to have Computer Science or Human-computer interaction. Alternatively, it's possible to move to UX engineering from design if a candidate is willing to learn to code. Such candidates should have a degree in design or psychology, but they should also demonstrate coding knowledge.
How long does it take to become a UX engineer?
It typically takes a few years to learn design and development spaces and gain practical experience to become a UX engineer. Most companies are looking for a person with 3+ years of experience in this area.
Is UX engineering a good career?
UX engineering is a promising career for anyone who wants to practice UX design and development. Development is an integral part of the UX engineering role. So if you like to write code and collaborate with designers and developers, this career is good for you.
What language do UX engineers use?
The languages UX engineers use can vary depending on the project they're working on. UX engineers are expected to be proficient in front-end development and, thus, should have a solid knowledge of HTML/CSS/JavaScript. UX engineers who participate in iOS projects are expected to have Swift skills.







 Turning design into code. Image by
Turning design into code. Image by 

